Enable hardware watchdog on RaspberryPi
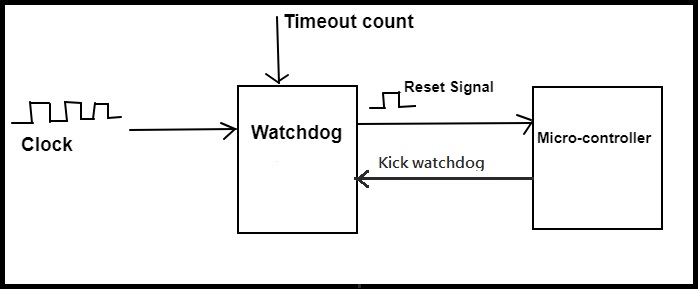
A watchdog timer is an electronic timer that is used to detect and correct computer malfunctions. When activated, it can trigger a reboot when the computer is under heavy load,
If the rpi fail to reset the timer before it expires, the WDT signal will reboot it. It is disabled by default in the firmware. Link
Users can set up “dtparam” also known as Device Tree config files for Raspberry Pi’s in /boot/config.txt, which will enable the kernel module.
Enable hardware dog
1
2
sudo su echo 'dtparam=watchdog=on' >> /boot/config.txt reboot
Install dog system service
Arch:
1
2
yay -S watchdog
1
2
3
Debian:
sudo apt-get install watchdog
Configure service
1
2
sudo su echo 'watchdog-device = /dev/watchdog' >> /etc/watchdog.conf
1
2
echo 'watchdog-timeout = 15' >> /etc/watchdog.conf
Note that Max interval for the raspberry 4 watchdog is 16 sec.
1
2
echo 'max-load-1 = 24' >> /etc/watchdog.conf
1
2
echo 'interface = wlan0' >> /etc/watchdog.conf
Enable service
1
2
sudo systemctl enable watchdog sudo systemctl start watchdog sudo systemctl status watchdog
To test the watchtog you could trigger a fork bomb
sudo bash -c ':(){ :|:& };:'
It is the responsibility of the user to set the parameters of the watchdog daemon correctly.
A common parameter that users set is the average CPU load for 1, 5, or 15 minutes. The default value for the 1 minute span is 24
max-load-1 = 24
The average load is the sum of the queue length and the number of jobs currently running on the CPUs.
You can use the following commands to view load average statistics:
uptime, procinfo, w, top
Raspberry Pi users who have the hardware watchdog enabled need to set a more appropriate value for the 1-minute span for the maximum load than the default value. As a workaround, you can log the average workload to a file:
1
2
3
4
5
6
#!/bin/bash
while true; do
echo $(cat /proc/loadavg) >> test_file.log
sleep 10
done
This will write a log with a timestamp every 10 seconds. Run the above script while performing intensive tasks that would normally trigger a reboot. With this information, you can now set a new value that is greater than the recorded maximum.